Flipped Learning Models: Impact In K-12 Education

What Is Flipped Learning?
A flipped classroom turns traditional teaching upside-down. Instead of teachers lecturing in class and students doing homework at home, students watch lessons at home and do activities in class. The idea behind the flipped classroom is to better use class time for active learning. When students come to class having already been introduced to the basic concepts, they can use that face-to-face time with the teacher (and with peers) to engage in deeper discussions, collaborative projects, and critical thinking exercises. It shifts the classroom from a passive learning environment to an active one.
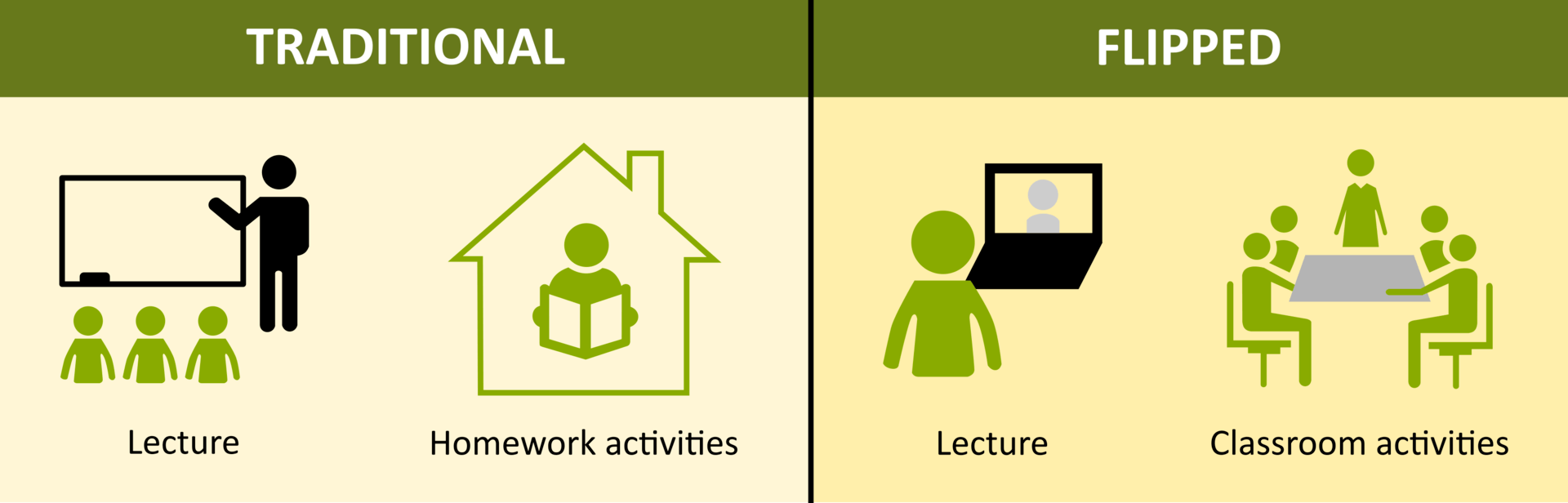
What Are The Different Types Of Flipped Learning Classroom Models?
Basic Flipped Classroom
- What it is
This is the foundational model of the flipped classroom. Students engage with lecture videos at home, taking the passive part of learning into their own hands. - In class
Once in the classroom, the real action begins. They’re no longer passive listeners. They engage in activities, collaborate with peers, discuss concepts, or clarify doubts with the teacher. - Why it works
This model breaks down the traditional wall of lecture in class and work at home, allowing students to digest new information at their own pace and then apply it interactively in class.
Discussion-Oriented Flipped Classroom
- What it is
This model takes the idea of classroom discussions to the next level. While students still learn foundational content at home, the in-class time is heavily discussion-driven. - In class
Students come prepared with questions, insights, or thoughts about their studies. They engage in debates, Socratic seminars, or roundtable discussions. - Why it works
This method promotes critical thinking and communication skills. By discussing topics, students refine their understanding and learn from multiple perspectives.
Demonstration-Based Flipped Classroom
- What it is
Ideal for hands-on subjects, this model has students grasp the theoretical part at home. - In class
Classroom time is dedicated to bringing those theories to life. For instance, after watching a video on photosynthesis, students might dissect a leaf in a biology class. In art, after studying a technique, they’d try it firsthand. - Why it works
Theory and practice go hand in hand. By applying what they’ve learned, students solidify their understanding and make real-world connections.
Group-Based Flipped Classroom
- What it is
Collaboration is at the heart of this model. While initial learning might happen individually, the classroom becomes a collaborative hub. - In class
Students work in teams, engaging in projects, problem-solving activities, or peer teaching. They learn from each other, capitalizing on each member’s strengths. - Why it works
Teamwork fosters a deeper understanding, allows for diverse perspectives, and builds essential soft skills like communication and cooperation.
Virtual Flipped Classroom
- What it is
This is the digital-age flipped classroom. Everything, from lectures to discussions, happens online. - In class
Instead of a physical classroom, students log into virtual spaces. They might watch a video, then join a virtual breakout room for discussions, or collaborate on a shared online document. - Why it works
It offers extreme flexibility. Students can learn from anywhere, anytime, and digital tools provide a range of innovative ways to engage with the material.
Steps To Implement Flipped Learning In K-12 Education
Leverage Technology
- Choose the right platforms for content delivery, be it video lectures, podcasts, or digital readings.
- Ensure that students have access to the necessary devices and a stable internet connection.
Create Engaging Content
- While third-party resources are available, teachers can also create personalized content tailored to their students’ needs.
- Interactive elements, such as quizzes or discussion prompts, can enhance engagement.
Redefine Classroom Activities
- Transition from lecture mode to facilitation.
- Introduce group discussions, hands-on projects, and problem-solving sessions.
Continuous Feedback
- Incorporate regular assessments to gauge understanding.
- Provide real-time feedback during in-class activities to address misconceptions.
Parental Involvement
- Educate parents about the flipped model to ensure home support.
- Share resources so parents can assist and engage in their child’s learning journey.
Professional Development For Teachers
- Continuous training ensures that educators are equipped with the skills and tools necessary for the flipped classroom.
- Encourage collaboration among teachers to share best practices and resources.
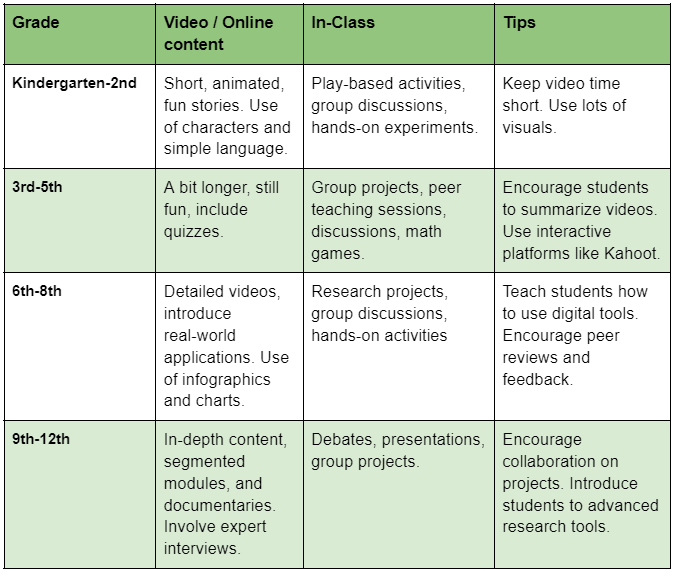
How To Use Flipped Classroom In Different Grades
In a study by Chou, Chen, and Hung (2021), flipped learning was shown to enhance both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation among high school students in Taiwan, compared to traditional teaching methods. The study further highlighted improvements in cognition, affection, and behavioral tendencies, emphasizing the effectiveness of flipped classrooms. This method varies depending on the age and needs of the students. Below is a guideline detailing how the flipped classroom model can be tailored for different grade levels, offering suggestions for online content, in-class activities, and some useful tips for educators:
Challenges Of Flipped Learning Models
While flipped classroom models are transformative in the educational landscape, several challenges can emerge:
- Digital divide
Not every student has consistent access to the necessary technology or a reliable internet connection at home, leading to potential inequalities in the learning experience. - Adaptation curve
Both educators and students require time and patience to adapt to the new paradigm, as it significantly deviates from traditional teaching methods. - Content creation
Developing effective and engaging content for students to study outside of the classroom is time-consuming and may require expertise or training. - Accountability and engagement
Ensuring that students engage with the content at home and come prepared for in-class activities can sometimes be a challenge, especially without established monitoring mechanisms. - Parental perception
Some parents, accustomed to conventional teaching methods, may need additional communication to understand and support this innovative approach.
Conclusion
Flipped classroom models, with their emphasis on active in-class learning and self-paced study, offer a promising avenue for modern education. They cater to varied learning styles, promote critical thinking, and foster a deeper understanding of concepts [1]. While challenges exist, the rewards in terms of student engagement, comprehension, and skill acquisition make it a compelling approach. As with any educational strategy, success lies in thoughtful implementation, regular assessment, and a willingness to adapt and evolve.
References:
[1] Learning Styles: Definition, Types, & Other InsightsImage Credits
- The images/tables within the body of the article have been created and supplied by the author.
Source link



